Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugai, Hiroyuki; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Fukuoka, Osamu*; Sataka, Masao; Kato, Teruo; Okayasu, Satoru; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Tazawa, Masato*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.291 - 294, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:70.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
 thin films irradiated with high-energy heavy ions
thin films irradiated with high-energy heavy ionsIshikawa, Norito; Yamamoto, Shunya; Chimi, Yasuhiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.250 - 253, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)Electronic excitation effects on TiO thin films with anatase structure irradiated with 230MeV Xe ions have been studied by means of X-ray diffraction method. X-ray diffraction intensity shows exponential decrease as a function of ion-fluence, indicating that tracks having about 10nm diameter are introduced by the irradiation. Rutile structured TiO
thin films with anatase structure irradiated with 230MeV Xe ions have been studied by means of X-ray diffraction method. X-ray diffraction intensity shows exponential decrease as a function of ion-fluence, indicating that tracks having about 10nm diameter are introduced by the irradiation. Rutile structured TiO was also irradiated and exhibited different damage behavior from that of anatase one. We demonstrated that X-ray diffraction meathod is one of the powerful tool to investigate track structure.
was also irradiated and exhibited different damage behavior from that of anatase one. We demonstrated that X-ray diffraction meathod is one of the powerful tool to investigate track structure.
Fukuoka, Osamu*; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Tazawa, Masato*; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Sataka, Masao; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.295 - 299, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobiyama, Mamoru*; Inami, Takashi*; Kambara, Tadashi*; Okuda, Shigeo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.171 - 175, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied effects of irradiation with energetic particles on defect accumulation in nanocrystalline gold (nano-Au). The specimens of nano-Au foil (3-5  m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV
m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV  C ions, 3.54-GeV
C ions, 3.54-GeV  Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production,
Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production, 
 , and annihilation,
, and annihilation, 
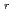 , in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E
, in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E , becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
, becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ono, Fumihisa*; Neumann, R.*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.161 - 165, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have performed swift heavy ion irradiations in Fe-50at.%Rh alloys at room temperature. Before and after the irradiations, the magnetic properties and the lattice structure are measured using Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) and X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD), respectively. We have also performed X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism (XMCD) measurement near the Fe K-edge at the synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, to examine the irradiation-induced ferromagnetic state near the specimen surface. We have found that the swift heavy ion irradiations induce the ferromagnetic state in Fe-50at.%Rh alloy below the antiferromagnetism-ferromagnetism transition temperature of the unirradiated alloy and the lattice expasion by 0.3%. For the specimens irradiated with swift heavy ions, we observe the XMCD spectra correponding to ferromagnetisim, which depend on the mass of irradiating ions and/or irradiation fluence. Effects of energy loss through electronic excitation and elastic collisions on lattice and magnetic structures of Fe-Rh alloy are discussed.
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au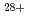 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.792, p.379 - 384, 2004/00
We have studied high-energy ion irradiation effects in bismuth by measuring the electrical resistivity at low temperature in relation to its structural change. Bismuth thin films (300-600  10 K with several kinds of energetic (100-200 MeV) heavy ions. The resistivity of the specimen is measured in-situ at
10 K with several kinds of energetic (100-200 MeV) heavy ions. The resistivity of the specimen is measured in-situ at  7 K during irradiation. After irradiation, annealing behavior of the resistivity is observed up to
7 K during irradiation. After irradiation, annealing behavior of the resistivity is observed up to  35 K. The temperature dependence of the resistivity during annealing shows an abrupt increase around 20 K, implying re-crystallization of irradiation-induced amorphous region. Since amorphous bismuth also shows a superconducting transition below
35 K. The temperature dependence of the resistivity during annealing shows an abrupt increase around 20 K, implying re-crystallization of irradiation-induced amorphous region. Since amorphous bismuth also shows a superconducting transition below  6 K, high-density electronic excitation due to energetic heavy-ion irradiation may induce columnar region of superconducting amorphous bismuth in normal crystalline bismuth. We are trying to detect the superconducting transition as a result of irradiation-induced amorphization.
6 K, high-density electronic excitation due to energetic heavy-ion irradiation may induce columnar region of superconducting amorphous bismuth in normal crystalline bismuth. We are trying to detect the superconducting transition as a result of irradiation-induced amorphization.
 O
O and MgO irradiated with energetic iodine ions
and MgO irradiated with energetic iodine ionsAruga, Takeo; Katano, Yoshio*; Omichi, Toshihiko*; Okayasu, Satoru; Kazumata, Yukio*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 197(1-2), p.94 - 100, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 O
O , MgAl
, MgAl O
O and MgO irradiated with energetic iodine ions
and MgO irradiated with energetic iodine ionsAruga, Takeo; Katano, Yoshio*; Omichi, Toshihiko*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Surface & Coatings Technology, 158-159, p.444 - 448, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kambara, Tadashi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 193(1-4), p.248 - 252, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Michikami, Osamu*; Wakana, Hironori*; Hashimoto, Takeo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 191(1-4), p.606 - 609, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Matsunami, Noriaki*; Sataka, Masao; Iwase, Akihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 193(1-4), p.830 - 834, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:83.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sekioka, T.*; Terasawa, Michitaka*; Sataka, Masao; Kitazawa, Shinichi; Niibe, M.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 193(1-4), p.751 - 754, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiation
superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiationSasase, Masato; Okayasu, Satoru; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi
Journal of Electron Microscopy, 51(Supple), p.S235 - S238, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
 produced by low energy Ne
produced by low energy Ne +He, Ne and Ar collisions
+He, Ne and Ar collisionsKitazawa, Shinichi; Ida, H.*; Matsui, Y.*; Takayanagi, Toshinobu*; Wakiya, K.*; Iemura, K.*; Otani, Shunsuke*; Suzuki, H.*; Kanai, Yasuyuki*; Safronova, U. I.*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 34(16), p.3205 - 3220, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.39(Optics)no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*
KEK Proceedings 2001-13, p.24 - 25, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*; Baba, Yuji
Surface Science, 482-485(Part.1), p.279 - 284, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
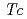 superconductor YBa
superconductor YBa Cu
Cu O
O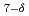 by high energy heavy ions
by high energy heavy ionsMatsunami, Noriaki*; Sataka, Masao; Iwase, Akihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 175-177, p.56 - 61, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Michikami, Osamu*; Wakana, Hironori*; Kambara, Tadashi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 69(11), p.3563 - 3575, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*; Baba, Yuji
Photon Factory Activity Report 1999, Part B, P. 325, 2000/11
no abstracts in English